Nutrition & Breastfeeding
Water/Drinks/Beverages
- Drink plenty of water during the day. The recommended daily fluid intake is 2.5 liters. The main source of fluids should be water. Other fluids that can help with daily hydration needs are milk, fruit and vegetable smoothies and beverages (excluding tea).
- Caffeine: Caffeine is absorbed into the mother’s blood and diffused in breast milk. Its high intake may cause irritation and insomnia to the newborn, while there is a higher likelihood of iron deficiency and gastrointestinal disorders. Drinking 1-2 caffeine beverages and, in general, a moderate daily consumption does not cause undesired caffeine levels in breast milk. Caffeine consumption should not exceed 200 mg/day.
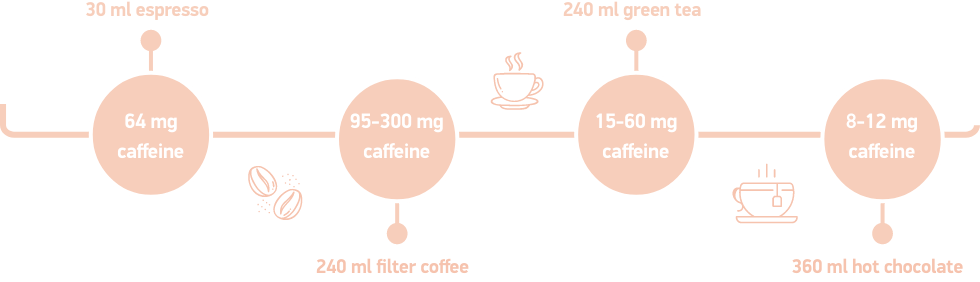
Indicative concentrations
- 30 ml espresso = 64 mg caffeine
- 240 ml brewed coffee = 95-300 mg caffeine
- 240 ml green tea = 15-60 mg caffeine
- 360 ml hot cocoa = 8-12 mg caffeine
Caffeine content may vary depending on the preparation of the beverages.
Dairy

Cow’s-milk protein allergy (CMPA) is the leading cause of food allergies in infants and children.
It is recommended to avoid cow and ewe milk dairy (e.g. goat milk, sheep or goat yogurt, sheep cheese such as feta, graviera, kasseri, etc. Read the nutrition facts label on the products you buy or ask the cheese department).
Information
As far as calcium intake is concerned, 950-1000 mg/daily is considered sufficient. Apart from dairy, wild edible greens, vine leaves, kale, okra, blanched almonds, tahini, sesame seeds, dried figs, sardines with bones, etc. are natural foods which are considered sources of calcium (i.e.>120 mg Ca/100 g).
Indicative dietary calcium sources

Fish
Fish intake should be ≥ 250 g a week. The recommended weekly consumption according to dietary guidelines is 360 g a week. Fish and shellfish provide high biological value proteins and other essential nutrients, they are low in bad saturated fats, while they are (especially the oily fish) a unique rich source of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (especially docosahexaenoic acid, DHA). Some of the fish that are rich in omega-3 are: sardines, mackerels, herrings, anchovies, cods, squids, etc.
When omega-3 fatty acids are obtained through diet, they increase the DHA levels in breast milk. Lipids in the brain are rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids, especially in DHA, and, therefore, they play a major role in brain development.
Information
Nearly all fish and shellfish contain traces of mercury. However, some fish contain higher levels of mercury which may harm the developing nervous system of an unborn baby, an infant or a child. The risk of mercury contamination from fish and shellfish depends on the quantity of the consumed food and the levels of mercury in this food.
Attention
Do not consume shark, swordfish, king mackerel, tilefish (Gulf of Mexico). Salmon, shrimps, all types of tuna, as well as the rest of fish and shellfish with low levels of methylmercury may be consumed.
As for consuming tuna: Consuming albacore tuna (canned tuna) and tuna steak should not exceed 180 g a week. Opt for Alonissos tuna or other types.
Vitamin D

In the event that the mother has vitamin D deficiency, breast milk has low vitamin D levels. It is important to have adequate sun exposure and nutritional intake of vitamin D (egg yolks, shiitake mushrooms, salmon and cod liver oil are good sources). In the event of inadequacy or deficiency of vitamin D, the administration of supplements is required.
Information
Check 25 (OH) D blood level. Target: 25 (OH)D > 30 ng / ml
Fruit and vegetables

Fruit and vegetables should be an important part of your daily diet (they are a high source of dietary fibers, vitamins, inorganic compounds, as well as antioxidants). The World Health Organization recommends at least 5 to 9 portions (400-600 g) of edible fruit and vegetables per day. In general, a portion of vegetables is equivalent to ½ cup of cooked vegetables and 1 portion of raw vegetables. A portion of fruit is equivalent to ½ cup of fruit juice or 1 medium fruit (approximately 100 g).
Information
By consuming a glass of fresh juice (2 portions of fruit), a salad with every meal (approximately 2 portions of vegetables) and 1-2 fruits in the morning (1-2 portions), you achieve your goal!